DHS Increases Premium Processing Fees
On February 26, 2024, the Department of Homeland Security will increase premium processing fees charged by U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS):
- From $1,500 to $1,685, for Form I-129, Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker, for H-2B and R-1 nonimmigrant status, and Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization, for certain F-1 students
- From $1,750 to $1,965, for Form I-539. Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status, for F-1, F-2, M-1, M-2, J-1, J-2, E-1, E-2, E-3, L-2, H-4, O-3, P-4, and R-2 nonimmigrant status
- From $2,500 to $2,805, for Form I-140, Immigrant Petition for Alien Workers, for employment-based classifications E11, E12, E21 (non-NIW), E31, E32, EW3, and recently available E13 and E21 (NIW)
A table in the final rule shows that overall, of those eligible for premium processing in fiscal years 2018 through 2022, 57 percent chose to submit a premium processing request:
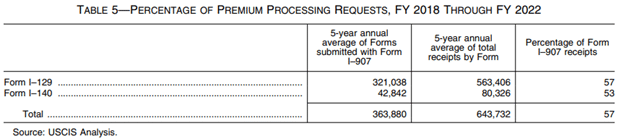
If USCIS receives a Form I-907 postmarked on or after February 26, 2024, with the incorrect filing fee, it will reject the Form I-907 and return the filing fee. For filings sent by commercial couriers (such as UPS, FedEx, and DHL), the postmark date is the date reflected on the courier receipt, USCIS said.
Details:
- USCIS alert (Dec. 27, 2023).
- USCIS final rule, 88 Fed. Reg. 89539 (Dec. 28, 2023).
State Dept. Announces Pilot Program to Resume Domestic H-1B Nonimmigrant Visa Renewals
On December 21, 2023, the Department of State (DOS) announced a pilot program to resume domestic visa renewal for qualified H-1B nonimmigrant visa applicants who meet certain requirements. The pilot program will accept applications from January 29 to April 1, 2024.
Participation in the pilot is limited to individuals who have previously submitted fingerprints in connection with an application for a prior non-diplomatic nonimmigrant H-1B visa, are eligible for a waiver of the in-person interview requirement, and meet other applicable requirements. DOS said the goal of the pilot is “to test the Department’s technical and operational ability to resume domestic visa renewals for specific nonimmigrant classifications and to assess the efficacy of this program in reducing worldwide visa wait times by shifting certain workloads from overseas posts to the United States.”
Applicants who meet the requirements can participate during the application window by applying online. Written comments and related materials must be received by midnight April 15, 2024.
Details:
- DOS notice, 88 Fed. Reg. 88467 (Dec. 21, 2023).
USCIS Updates Policy Guidance for International Students
On December 20, 2023, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) issued policy guidance regarding F and M nonimmigrant students, including the agency’s role in adjudicating applications for employment authorization, change of status, extension of stay, and reinstatement of status for these students and their dependents in the United States. USCIS said it “expects that this will provide welcome clarity to international students and U.S. educational institutions on a wealth of topics, including eligibility requirements, school transfers, practical training, and on- and off-campus employment.”
For example, USCIS said, the guidance clarifies that F and M students must have a foreign residence that they do not intend to abandon, but such a student may be the beneficiary of a permanent labor certification application or immigrant visa petition and may still be able to demonstrate an intent to depart after a temporary period of stay.
In addition, the guidance specifies how an F student seeking an extension of optional practical training based on a degree in a science, technology, engineering, or mathematics field may be employed by a startup company, as long as the employer adheres to the training plan requirements, remains in good standing with E-Verify, and provides compensation commensurate to that provided to similarly situated U.S. workers, among other requirements.
Details:
- USCIS alert (Dec. 20, 2023).
- USCIS policy alert, PA-2023-34 (Dec. 20, 2023).
State Dept. Expands Consular Authority for Nonimmigrant Visa Interview Waivers
On December 21, 2023, the Department of State (DOS) announced that it had consulted with the Department of Homeland Security and determined that several categories of interview waivers are in the national interest. As of January 1, 2024, consular officers will have the discretion to waive the in-person interview for:
- First-time H-2 visa applicants (temporary agricultural and nonagricultural workers) and
- Other nonimmigrant visa applicants applying for any nonimmigrant visa classification who:
- Were previously issued a nonimmigrant visa in any classification, unless the only prior issued visa was a B visa; and
- Are applying within 48 months of their most recent nonimmigrant visa’s expiration date.
Consular officers may still require in-person interviews on a case-by-case basis or because of local conditions. DOS encourages applicants to check embassy and consulate websites.
Details:
- DOS notice (Dec. 21, 2023).
USCIS Reaches FY 2024 H-1B Cap
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) announced on December 13, 2023, that it has received a sufficient number of petitions needed to reach the congressionally mandated 65,000 H-1B visa regular cap and the 20,000 H-1B visa U.S. advanced degree exemption, known as the master’s cap, for fiscal year (FY) 2024.
USCIS said it will send non-selection notices to registrants through their online accounts. When the agency finishes sending the non-selection notifications, the status for properly submitted registrations that USCIS did not select for the FY 2024 H-1B numerical allocations will show:
- Not Selected: Not selected—not eligible to file an H-1B cap petition based on this registration.
USCIS said it will continue to accept and process petitions that are otherwise exempt from the cap. Petitions filed for current H-1B workers who have been counted previously against the cap, and who still retain their cap number, are exempt from the FY 2024 H-1B cap. USCIS will continue to accept and process petitions filed to:
- Extend the amount of time a current H-1B worker may remain in the United States;
- Change the terms of employment for current H-1B workers;
- Allow current H-1B workers to change employers; and
- Allow current H-1B workers to work concurrently in additional H-1B positions.
Details:
- USCIS alert (Dec. 13, 2023).
District Court Rules in College’s Favor in EB-1 Case
In Scripps College v. Jaddou, a U.S. District Court in Nebraska held that U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) improperly denied the plaintiff’s I-140 immigration petition when it found that the beneficiary of the petition did not qualify for an employment-based first preference visa as an “outstanding professor or researcher.” The court ruled in favor of the plaintiff, Scripps College.
Scripps argued that USCIS’s denial of its I-140 petition must be reversed because USCIS made internally inconsistent findings, imposed novel evidentiary requirements, disregarded relevant factors, and was not supported by substantial evidence.
Citing various decisions, the court noted that agency action must be upheld on review unless it is “arbitrary, capricious, an abuse of discretion, or otherwise not in accordance with the law.” An agency decision is arbitrary and capricious if the agency acted outside “the bounds of reasoned decision-making, relied on factors which Congress has not intended it to consider, provided an explanation that runs counter to the evidence, or makes a decision that is so implausible that it could not be ascribed to a difference in view or the product of agency expertise,” the court noted.
Among other things, the court found that USCIS had made inconsistent findings based on the evidence, and made findings that were controverted by the evidence. Further, the court said, the “unexplained internal inconsistencies” reflected that USCIS failed to articulate a satisfactory explanation for its action, including “a rational connection between the facts found and the choice made.” USCIS also “imposed novel evidentiary requirements in its denial” of Scripps’ I-140 petition, the court said. Concluding that USCIS’s decision “was arbitrary and capricious, an abuse of discretion, and contrary to the law,” the court granted Scripps’ motion for summary judgment and denied USCIS’s motion for summary judgment.
Details:
- Scripps College v. Jaddou (Dec. 12, 2023).
ETA Seeks Information on STEM and Non-STEM Occupations in PERM Schedule A
The Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (ETA) is seeking information from the public to potentially consider revisions to Schedule A of the permanent labor certification process to include occupations in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), including Artificial Intelligence-related occupations, and non-STEM occupations, for which there may be an insufficient number of ready, willing, able, and qualified U.S. workers.
ETA said its request for information (RFI) will provide the public an opportunity to address whether and why STEM occupations should be added to Schedule A, offer information on which occupations should be considered as falling under the umbrella of STEM, and request data, studies, and related information that should be considered to establish a reliable, objective, and transparent methodology for identifying STEM or non-STEM occupations with a significant shortage of workers that should be added to or removed from Schedule A. “To the extent possible and wherever appropriate, responses to this RFI should indicate the question number(s) and include specific information, data, statistical models and metrics, and any resources relied on in reaching conclusions for its claims, rather than relying on general observations,” ETA said.
Details:
- PERM Schedule A Request for Information, announcement, Dept. of Labor (Dec. 15, 2023).
- Request for Information (advance copy), Labor Certification for Permanent Employment of Foreign Workers in the United States; Modernizing Schedule A to Include Consideration of Additional Occupations in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) and Non-STEM Occupations.
USCIS Changes Filing Location for Form I-907 Filed for Pending Form I-140
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) announced that as of December 15, 2023, it has begun transitioning the filing location for Form I-907, Request for Premium Processing, when filed for a pending Form I-140, Immigrant Petition for Alien Workers, from the service centers to appropriate USCIS lockboxes.
USCIS noted that this change does not apply to those filing Form I-140 concurrently with an associated application (such as Form I-485, I-765, or Form I-131). The agency said it will soon announce a filing location change for these forms, but as of now, such forms should be filed with the service centers as listed on the Direct Filing Addresses for Form I-140, Immigrant Petition for Alien Worker page.
USCIS will reject any Form I-907 filed with Form I-140 that is received at the previous service center address.
Details:
- USCIS alert, including new lockbox addresses (Dec. 13, 2023).
- USCIS Tips for Filing Forms by Mail (last reviewed/updated Dec. 13, 2023).
USCIS Releases Employment-Based Adjustment of Status FAQs
On December 8, 2023, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) released frequently asked questions (FAQs) about employment-based (EB) adjustment of status.
USCIS noted that the EB annual limit for fiscal year (FY) 2024 will be higher than was typical before the pandemic, but lower than it was in FYs 2021-2023. USCIS said it is dedicated to using as many available employment-based visas as possible in FY 2024, which ends on September 30, 2024.
Details:
- USCIS FAQs (Dec. 8, 2023).
State Dept. Issues Final Rule to Eliminate Informal Evaluations of Immigrant Visa Applicants’ Family Members
Effective January 8, 2024, the Department of State (DOS) is amending its immigrant visa regulations by removing the section allowing a consular officer to conduct an informal evaluation of the family members of an immigrant visa applicant to identify potential grounds of ineligibility.
DOS explained that the existing regulation was promulgated in 1952, when a consular officer could more readily assess a family member’s potential qualification for a visa without a formal visa application. “Assessing eligibility for an immigrant visa is now a more complex task and not one which can be accomplished accurately with an informal evaluation,” DOS said.
Details:
- DOS Final Rule, 88 Fed. Reg. 85109 (Dec. 7, 2023).
Klasko News
FIRM NEWS
Klasko Immigration Law Partners is excited to welcome Timothy D’Arduini as its newest attorney and partner. Welcome, Tim!
IN THE NEWS
Timothy D’Arduini
Law360 interviewed Klasko Immigration Law Partners newest partner and attorney, Timothy D’Arduini.
RECENT SPEAKING ENGAGEMENTS
H. Ronald Klasko
On December 1st, Ron Klasko spoke at the ILCA 2nd Annual Immigration Policy and Advocacy WebCLE on a panel titled Foreign Investment Incentives and Hurdles.
Michele Madera
On December 4th, Michele Madera spoke at this AILA NY Symposium event on a panel titled Sunset Boulevard: Is the Golden Age of PERM Over?
Michele Madera
On December 13, Michele Madera spoke at an AILA Philadelphia event on PERM Updates and Hot Topics from 2023.
ICYMI: RECENT BLOG POSTS AND ALERTS
Department of State Pilot Program Allowing Stateside Renewal of Certain H-1B Visas Begins January 29, 2024
In this client alert, Elise Fialkowski covers the pilot program announced by the DOS to resume domestic visa renewal for certain H-1B visa holders.
Klasko Immigration Law Partners Announces 2024 Leadership Changes
This publication announces several exciting new leadership changes at Klasko Immigration Law Partners.
Employers Seeing the Benefits of Using E-Verify As Program Modernizes
In this article, Carolina Regales informs that the final rule has now created a permanent optional remote I-9 verification process for E-Verify participants who are in good standing.
Klasko Immigration Law Partners Welcomes Timothy D’Arduini as New Partner and Expands Into Washington, DC
This publication announces Klasko Immigration Law Partners newest attorney and partner, Timothy D’Arduini.
FIRM FEATURE
Happy Holidays and a Happy New Year, from your friends at Klasko Immigration Law Partners.

Stay Connected! Subscribe to our blog and follow us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
This newsletter was prepared with the assistance of ABIL, the Alliance of Business Immigration Lawyers, of which Klasko Immigration Law Partners is an active member.
